
一种多通道微流控芯片,用于筛选对宫颈癌细胞具有最大趋向性的不同来源间充质干细胞。
Introduction
宫颈癌是全球最常见的妇科恶性肿瘤之一,严重威胁着妇女的健康。长期以来,化疗一直被用于宫颈癌的治疗。然而,传统的化疗药物通过全身循环给药,存在吸收有限、血液清除快、多器官毒性大等严重缺点。虽然人工合成的纳米颗粒(NPs)已被设计用于给药,并具有更强的渗透性和保留效果,但这些给药系统通常需要复杂的功能化处理,以实现与生物环境的最佳相互作用,从而确保特异性给药并避免免疫清除。 但也存在细胞膜来源有限、制备过程复杂、过度使用免疫细胞膜可能引发炎症的问题,这些都给细胞膜包膜载体的临床应用带来了挑战。
在本文中提出了一种用于药物封装和癌症靶向治疗的滋养间充质干细胞(MSCs)筛选的微流控平台,如图1所示。间充质干细胞因其对肿瘤龛位的独特滋养作用而被用作抗癌药物载体。虽然来自不同组织的间充质干细胞具有相似的形态和免疫表型,但不同间充质干细胞的归巢能力可能存在差异,并具有组织特异性。 肿瘤芯片为再现复杂的肿瘤微环境提供了一个强大的体外平台。然而,在微流控芯片中筛选具有肿瘤滋养特性的间充质干细胞的研究仍然较少。此外,将筛选出的间充质干细胞膜(MSCMs)用作药物输送载体的研究仍然很少。
在此开发了一种含有Matrigel的多通道微流控芯片,用于比较不同间充质干细胞对宫颈癌细胞的滋养作用。该装置由九个独立的微流道组成,其中四个微流道中填充了Matrigel支架作为侵袭室。通过在中心流道中培养宫颈癌细胞,在不同侧道中培养每种间充质干细胞,该芯片实现了间接接触共培养和实时观察细胞侵袭而不会造成物理损伤。在芯片上筛选出对宫颈癌细胞具有最强归巢能力的间充质干细胞。在此基础上,提取了间充质干细胞来封装药物载荷的NPs,结果表明这种NPs具有很强的肿瘤靶向能力。此外还证实了包覆药物载体的MSCMs在体内治疗宫颈癌的疗效。这些结果表明,微流控平台在筛选用于癌症靶向治疗的功能性间充质干细胞方面极具潜力。
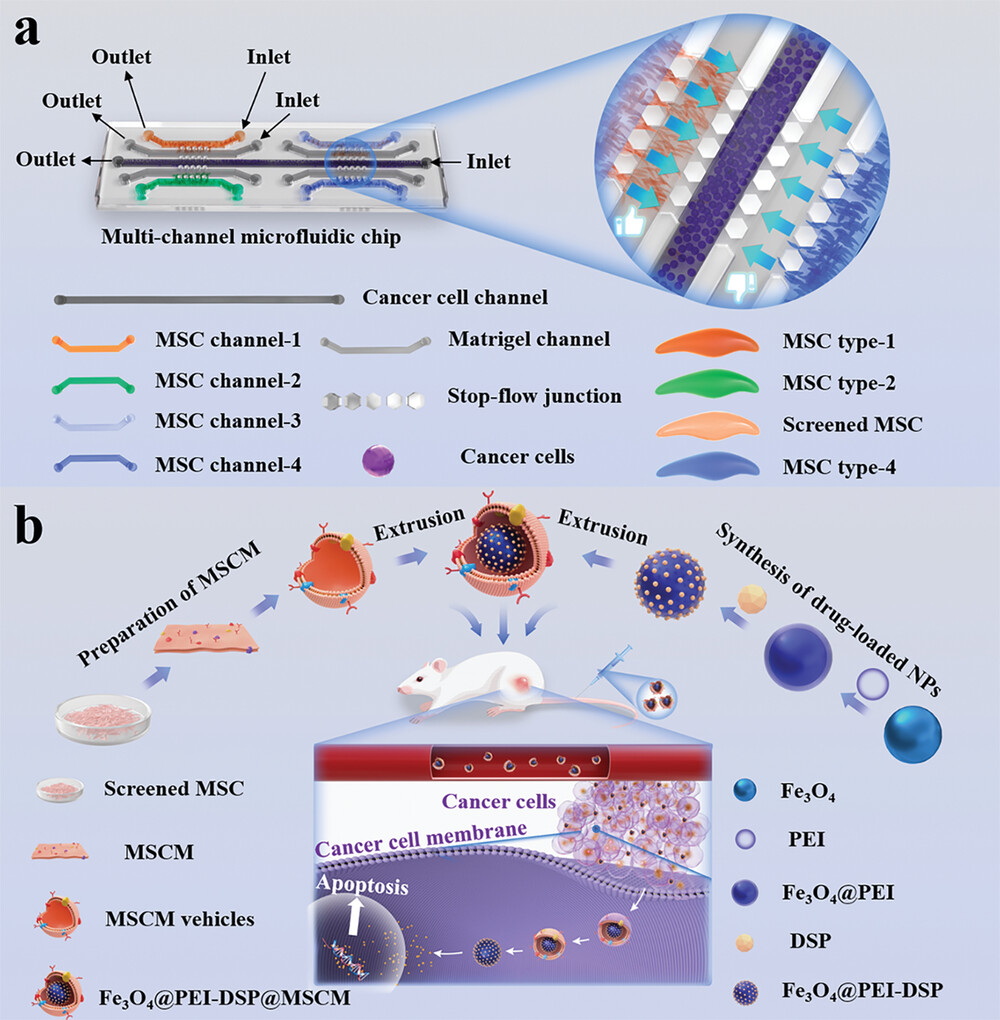
(a)筛选具有肿瘤生长能力的不同间充质干细胞的微流体平台示意图。
- (b)制备用于宫颈癌化疗靶点治疗的经筛选的间充质干细胞-伪装纳米系统示意图。
Tropism of MSCs toward cervical cancer cells on the microfluidic device

- (a-d)(a)羊膜(AM-MSC)、(b)脂肪组织(AT-MSC)、(c)绒毛膜(CP-MSC)和(d)脐带(UC-MSC)的侵袭行为。间充质干细胞由CellTracker Red染色。SiHa和Ect1/E6E7细胞由CellTracker Red染色。
- (e-f)Matrigel区域不同间充质干细胞对DMEM、SiHa、Ect1/E6E7细胞的(e)侵袭面积和(f)最长侵袭距离统计。在四种间充质干细胞类型中,CP-MSC对SiHa细胞的趋向性行为最强,这些结果验证了间充质干细胞对宫颈癌的特异性趋向作用,并表明CP-MSC是最有希望用于宫颈癌治疗的候选药物。
Construction and characterization of the NPs

作者选择了Fe3O4 NPs作为药物载体,并对其进行了适当修饰,以负载铂原药(DSP),该原药是为降低顺铂的毒性作用而合成的,并经核磁共振分析证实。然后在表面修饰聚乙烯亚胺(PEI),经振荡孵育后得到 Fe3O4@PEI(以下称 NP-2)。随后,用DSP对NP-2进行装饰,制备出Fe3O4@PEI-DSP(以下简称 NP-3)。最后,用从CP-MSC中纯化的MSCMs对NP-3进行伪装,制备出功能化的Fe3O4@PEI-DSP@MSCM NP(以下简称 NP-4)。
- (a)(i)NP-1、(ii)NP-2、(iii)NP-3 和(iv)NP-4 的TEM图像。NPs的平均直径分别为100.6(NP-1)、105.2(NP-2)和 106.2 nm(NP-3)。
- (b) (i)NP-3的高角度环形暗场扫描透射电子显微镜(HAADF-STEM)图像和(ii-vi)NP-3 的元素映射图像:(ii)Fe元素,(iii) O元素,(iv)N元素,(v)Pt元素,(vi)合并。铁元素局限于NP-3的核心,而铂元素只存在于表面,这证实了药物负载的成功。封装MSCM后,NP-4呈典型的核壳结构,直径≈111.8 nm。表面的MSCM层厚度约为4.8 nm。
- (c)通过动态光散射(DLS)测量的NPs流体力学尺寸。
- (d)NPs的Zeta电位。NP-1在ddH2O中的表面电荷为-37.3 ± 2.1 mV。NP-2的zeta电位变为正值36.6 ± 5.5 mV,这意味着PEI已成功包覆在NP-1表面。载入DSP后,NP-3的zeta电位降至28.0 ± 2.0 mV,表明药物共轭成功。此外,NP-4的zeta电位在修饰MSCM后变为-39.5 ± 0.5 mV,与MSCM保持同等水平。
- (e)经柯马西蓝(Coomassie)染色后的凝胶SDS-PAGE图像。表明NP-4具有与MSCM相似的蛋白质特征,但与间充质干细胞裂解物的蛋白质特征略有不同。此外,NP-4制作过程中保留了大部分膜蛋白成分,表明MSCM已成功包被。
- (f)通过流式细胞术分析NP-4上的MSCM特异性标记CD73、CD90和CD105。表明NP-3表面被MSCM所覆盖。
- (g-h)在不同时间测量的NP-4在纯PBS和含10% FBS的PBS中的粒径和多分散指数(PDI)。表明了NP-4在生物环境中出色的生理稳定性。
In vitro antitumor ability of composite NPs on SiHa cells

- (a)NP-1或NP-1@MSCM培养4 h后SiHa细胞的普鲁士蓝染色(评估癌细胞对铁的吸收)。结果发现,蓝染的NPs主要分布在 SiHa细胞核周围的细胞质中。更重要的是,与裸露的NP-1相比,MSCMs伪装的 NP-1(NP-1@MSCM)培养的细胞显示出更强的铁染色强度,这表明MSCM伪装有助于增强内化效应。
- (b)通过流式细胞术进行细胞凋亡分析。在与游离DSP、NP-3或NP-4培养24 h后,SiHa细胞的活力受到明显抑制。此外,NP-4 处理24 h后的细胞活力低于NP-3培养的细胞活力,这是因为MSCM包被后NPs的吸收能力增强。共培养48 h后,DSP组、NP-3组和NP-4组SiHa细胞的存活率进一步下降,降幅相同。这是因为所有类型的NPs都完全渗透到了细胞中,DSP在细胞内大量释放。
- (c)经DSP、NP-3或NP-4处理的SiHa细胞的活体/死体染色图像。结果发现,SiHa细胞对NP-3敏感,而对NP-4的杀伤效果更为明显。
- (d)通过流式细胞术分析细胞凋亡。SiHa细胞与DSP、NP-3或NP-4共同培养。NP-3处理24和48 h后,SiHa细胞的凋亡率分别为 17.9%和42.6%,经MSCM掩蔽后,凋亡率进一步提高。总之,细胞毒性测试结果表明,MSCM-伪装纳米载体对宫颈癌细胞具有很强的杀伤作用。
In vivo antitumor performance of composite NPs in SiHa cancer-bearing mice

- (a)动物实验方案示意图。在雌性裸鼠的右腋下注射SiHa细胞,建立肿瘤异种移植模型。5 week后,小鼠被随机分为六组。分别从小鼠尾静脉注射PBS、DSP和复合NPs(NP1-4)。DSP组、NP-3组和NP-4组的铂注射剂量为2 mg kg-1体重;NP-1组和NP-2组的铁注射剂量为36.2 mg kg-1,与NP-3组和NP-4组相同。各组的注射时间分别为第 0、7、14、21和 28 d。每4 d对每只小鼠进行一次肿瘤大小和体重测量,结果表明,PBS组的肿瘤生长迅速,而NP-1和NP-2组的肿瘤生长趋势受到轻微抑制。这表明积累的铁在体内也具有部分肿瘤毒性。此外,DSP和NP-3对肿瘤生长的抑制作用更大。这表明DSP和NP-3可通过被动靶向作用在肿瘤部位积累到一定程度。此外,NP-4组的抑瘤效果在各组中最好,这是因为NP-4的循环时间长且具有主动靶向作用,从而增强了化疗效果。
- (b)不同处理的裸鼠肿瘤样本图像。
- (c-d)第32 d测量的各组(c)肿瘤大小和(d)重量。
Evaluation of the role of the composite NPs in inhibiting tumor growth and promoting apoptosis in vivo

- (a)通过H&E染色显示不同处理后小鼠肿瘤组织的图像。
- (b)通过IHC染色显示不同处理后肿瘤组织中Ki-67的代表性图像。
- (c)通过末端脱氧核苷酸转移酶dUTP缺口标记(TUNEL)染色显示不同治疗方法下小鼠肿瘤组织的图像。
- (d)通过H&E染色对细胞数进行定量。
- (e)对肿瘤组织中Ki67阳性细胞进行定量。NP-4治疗后,癌组织中的Ki-67阳性染色较弱,表明NP-4组的细胞增殖水平低于其他组。
- (f)通过TUNEL检测对肿瘤组织中的凋亡细胞进行定量。表明NP-4比其他治疗方法诱导了更多的肿瘤细胞凋亡。这些结果共同表明,NP-4是一种有效的给药载体,可以增强宫颈癌的化疗效果。
Conclusion
- 开发了一种Matrigel结合微流控芯片,用于筛选来自不同组织的人体间充质干细胞。该芯片由一个可容纳宫颈癌细胞的中央通道、四个装有Matrigel支架的侵袭室和四个独立的侧通道组成,四种类型的间充质干细胞在侧通道中培养。经芯片鉴定,CP-间充质干细胞对宫颈癌细胞的趋向能力最强。在此基础上,提取了“CP-MSC”膜用于药物递送。由顺铂合成的铂原药DSP被载入 Fe3O4@PEI NPs,载药NPs进一步被细胞膜伪装,用于宫颈癌的靶向治疗。
- 结果表明,复合纳米系统具有良好的生物相容性,细胞膜涂层有助于增强细胞内化。更重要的是,复合纳米系统对SiHa细胞的生长具有抑制作用。本微流控平台为筛选滋养间充质干细胞提供了一种有效的方法,而间充质干细胞衍生的载药纳米系统有望用于宫颈癌的靶向化疗。
Reference
Song Y, Shou X, Sheng B, et al. Cell Membranes from Tumor-Tropic MSCs Screened by a Microfluidic Chip for Drug Nanoparticles Encapsulation and Cancer Targeted Therapy[J]. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 2023, 12(17): 2202904.



